eBUS Adapter Shield C6 Stick Edition
The “Stick” edition is the tiny brother of the eBUS Adapter Shield with a 30 % smaller footprint of only 42x16mm in the shape of a USB stick and I/O capabilities reduced to the most commonly used options (i.e. a USR-ES1 Ethernet module on top and/or some sensors).
You can get the stick here:
Introduction
Just like its big brother, the stick edition fulfils the arbitration times required by the eBUS specification. This is made possible by the use of an ESP32-C6 in RISC architecture which, among other things, brings the following advantages:
- minimal time delay due to specially developed driver in the firmware
- full galvanic isolation with zero power drawn from eBUS (class 0 as of eBUS specification)
- flexible, configurable connection to the host:
- full support for ebusd enhanced protocol and standard protocol
- via web browser configurable and also updatable firmware by OTA update as well as directly via USB JTAG/serial
- tested to all requirements for CE marking
- many further possibilities, e.g. connection with sensors and/or displays.
Of course it also uses a DC-DC converter and galvanic isolation in order to have the eBUS completely isolated from the host and thus draws only marginal current from the eBUS without any fluctuation (class 0 according to specification chapter 10.7).
This way, the heating, ventilation or solar system is perfectly protected and is not burdened in any way on its own power source.
Connections
This is an overview of the individual components and their connections:

- Heating/ventilation/solar thermal system
is connected to the adapter via a 2-wire cable (the polarity does not matter). - Adapter
connected to ebusd either via - ebusd
interprets the eBUS protocol and provides the data bidirectionally via MQTT, HTTP, KNX, and TCP port for Home-Assistant, KNX, Node-Red, FHEM, and others.
Host connection
Connecting via USB and WIFI is always possible. Only the Ethernet connection requires an additional USR-ES1 module.
By using the easi> interface (via USB or network) all parameters can be adjusted.
Upon delivery, the firmware might need to be installed first, see under first steps.
The protocol between ebusd and the adapter is either the eBUS protocol directly (“standard protocol”) or the ebusd “enhanced protocol”. The enhanced protocol uses all advantages of the adapter by handling the eBUS arbitration directly from the firmware.
WIFI

To use the adapter via WIFI, it just needs to be connected to a power source using the USB connector.
By using the easi> interface, the host connection needs to be set to WIFI (preset for a new or no yet configured adapter). It can also be used to adjust the WIFI configuration (SSID, DHCP/fix IP address, network mask, gateway).
The initial WIFI setting can be done either via the firmware page, the “EBUS” access point, or via WPS with push button mode (PBC; as long as the adapter has not yet been configured and the button is pressed once so that the red LED is on permanently).
In addition to the adapter, only a regular USB cable/adapter with a USB-C plug is needed. The eBUS adapter comes with an eBUS connector already plugged in.
The power is supplied directly via the USB connector.
The ebusd device configuration is e.g. -d ens:192.168.178.2:9999, where 192.168.178.2 has to be replaced with the
right IP address.
USB
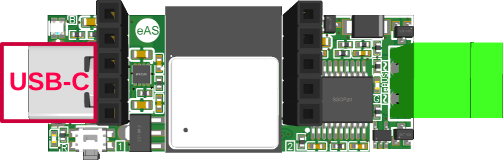
To use the adapter via USB, it just needs to be connected with the host using the USB connector.
All modern operating systems (Windows/Linux/MacOS) already have the necessary driver for that.
The adapter provides two interfaces on USB, that are presented as product “USB JTAG/serial debug unit” (idProduct: 0x1001) of “Espressif” (idVendor: 0x303a):
- Interface 0 (incl. 1): CDC ACM (USB “communication device class” with “abstract control model”)
the serial interface, appears as “USB ACM device” on Linux in/dev/ttyACM<x>, and as “USB JTAG/serial debug unit (interface 0)” or “Serial USB device (COM…)” on Windows - Interface 2: JTAG Debug
the Debug interface, does not appear as a device in/devon Linux (lsusb -treports it as “If 2, Class=Vendor Specific Class” without driver), and as “USB JTAG/serial debug unit (interface 2)” on Windows (this is unused)
By using the easi> interface, the host connection needs to be set to USB.
In addition to the adapter, only a regular USB cable/adapter with a USB-C plug is needed. The eBUS adapter comes with an eBUS connector already plugged in.
The power is supplied directly via the USB connector.
The ebusd device configuration is e.g. -d ens:/dev/ttyACM0, where ttyACM0 might be different when several
USB devices of this kind are connected.
Ethernet
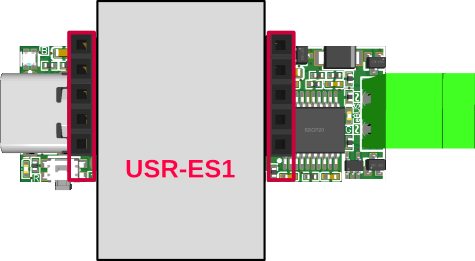
To use the adapter via Ethernet, a
USR-ES1 Module with W5500 (e.g. from here or here)
needs to be plugged in to the pin headers 1+2.
Attention: when the USR-ES1 module is not correctly plugged onto the adapter (e.g. shifted or in the wrong direction), the adapter can be damaged and become unusable! So the best way it to disconnect power, plug in the module, and check the position. After that, power can be reconnected.
When a USR-ES1 module is plugged in, it looks like this:
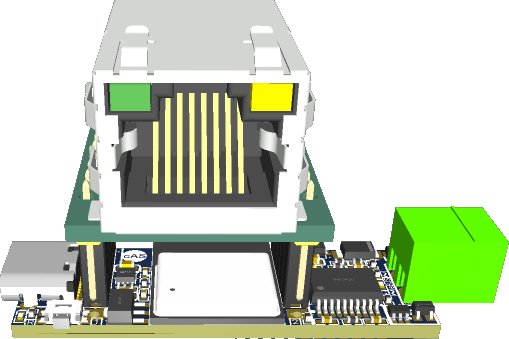

By using the easi> interface, the host connection needs to be set to Ethernet. It can also be used to adjust the Ethernet configuration (DHCP/fix IP address, network mask, gateway).
If the USR-ES1 module cannot be detected by the firmware, it might be broken or ideally only the pin connection is not stable. See here for checking this.
In addition to the adapter and the USR-ES1 module, only a regular USB cable/adapter with a USB-C plug is needed. The eBUS adapter comes with an eBUS connector already plugged in.
The power is supplied directly via the USB connector.
The ebusd device configuration is e.g. -d ens:192.168.178.2:9999, where 192.168.178.2 has to be replaced with the
right IP address.
Power Source
When using Ethernet or WIFI as the host connection, the adapter is simply powered via the USB connector using a standard USB power adapter, e.g. one that can also be used to charge a cell phone.
The minimum requirement for the power source is 1 Watt. To be on the safe side, we recommend using a power source with at least 2 Watts, i.e. capable of supplying 400mA at 5V.
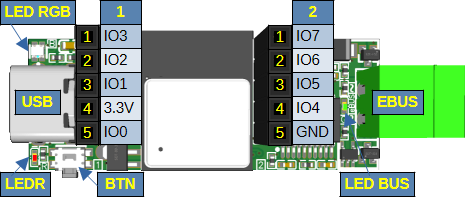
Pin headers, functions
Additional pin headers are available for connecting further components. With Ethernet only a small number of pins are available for that.
| Connector | Function | USB | WIFI | Ethernet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USB | USB connector | USB | power | power |
| 1 | I/O / W5500 | I/O | I/O | W5500 |
| 2 | I/O / W5500 | I/O | I/O | W5500 |
| EBUS | eBUS connector | eBUS | eBUS | eBUS |
The easi> interface can be used to associate a pin with an I/O function.
I/O pinout
The ESP32-C6 I/O pins are associated and available on headers as follows:
| IO | Function / Header/Pin | Setting | USB + WIFI | Ethernet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1/5 | * | 3.3V | |
| 1 | 1/3 | * | - | |
| 2 | 1/2 | * | RST | |
| 3 | 1/1 | * | MISO | |
| 4 | 2/4 | * | MOSI | |
| 5 | 2/3 | * | SCLK | |
| 6 | 2/2 | * | SCNN | |
| 7 | 2/1 | * | INTN | |
| 9 | Button | pull-up | - | - |
| 12 | USB- | USB | - | |
| 13 | USB+ | USB | - | |
| 14 | eBUS RX | - | - | |
| 15 | eBUS TX | - | - | |
| 16 | TX, LED red | 500R | LED | LED |
| 23 | LED RGB | LED RGB | LED RGB |
Legend:
- * = any function assignment
- - = not usable otherwise
LEDs
The adapter has a red LED and a RGB LED with the following assignment, as well as a green eBUS-LED:
- RGB LED: signals from firmware
- red LED: eBUS send or firmware signal
- green eBUS-LED: eBUS reception and eBUS voltage level
During boot all LEDs fade three times (except for the green eBUS-LED). In that phase, pressing the button allows to ignore all saved settings and start the WIFI access point with SSID “EBUS”.
In eBUS mode, the blue LED blinks shortly every 5 seconds as a ping, when configured like that via easi> interface.
The RGB LED lights up in red during writes on eBUS, when eBUS mode is on and configured like that via easi> interface.
The green eBUS-LED has several functions:
- permanently on when eBUS is not connected: adapter power supply is OK
- permanently off when eBUS is connected: eBUS voltage level is OK, but no traffic
- Flashing when eBUS is connected: eBUS voltage level is OK with traffic
Button
The adapter has a button on board allowing several actions:
- press+hold before powering up:
bootloader mode - press+hold during boot (while the LEDs fade):
ignore all saved settings and start the WIFI access point “EBUS” - press after boot:
- as long as the adapter has not yet been configured: start WPS in push button mode (PBC, red LED is on permanently until successfully connected)
- otherwise: red LED fades once
- press+hold after boot:
reboot
Links
Here are some links that contribute to the topic or contain basic information: